In the field of plastic molding, blow molding and rotational molding are often mentioned together, but their underlying logic is completely different. Simply put: blow molding involves "blowing," while rotational molding involves "turning."
This seemingly minor difference brings about a world of difference in principles, costs, and final product performance. If you are looking for the most economical and reliable solution for your project—whether it's a delicate packaging bottle or a large storage tank—a deep understanding of this "blowing" versus "rotational" competition is crucial.
Blow molding and rotational molding are the two main processes for manufacturing hollow plastic products, and they differ fundamentally in principle, product characteristics, and application scenarios. Below, I will provide a clear comparison using a table, followed by a detailed explanation.
Comparative Overview: Blow Molding vs. Rotational Molding
| Feature Dimension | Blow Molding | Rotational Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | "Blowing": A heated plastic parison is inflated with high-pressure air against the mold cavity walls and cooled. | "Rotating": Plastic powder is heated in a rotating mold, melts, and coats the inner walls uniformly before cooling. |
| Material Form | Molten plastic melt (extruded or injected as a tubular parison) | Plastic powder (most commonly polyethylene PE powder) |
| Mold | Usually a two-part mold, must withstand high pressure; made of steel or aluminum — high cost. | Single-piece or simple split mold, no high-pressure resistance; made of thin sheet metal — lower cost. |
| Wall Thickness Control | Less uniform (especially in extrusion blow molding); parison sag leads to thicker bottom, thinner top. | Highly uniform, controlled precisely by powder weight and rotation speed. |
| Product Characteristics | - High surface finish, sharp detail - Has parting lines that require trimming - Can produce transparent/translucent items | - Seamless, no joints, one-piece construction - Low internal stress, high impact resistance - Usually opaque - Consistent thickness in corners |
| Size Range | From small bottles (few mL) to large industrial drums (e.g., 200L oil barrels) | Ideal for large/extra-large products — from toys to tanks holding tens of thousands of liters, boat hulls. |
| Design Flexibility | High; can produce complex shapes, with handles, irregular geometries. | Very high; can create highly complex, double-walled, or internally fitted parts — almost no design limits. |
| Production Efficiency | Very high, suitable for high-volume continuous production (especially extrusion blow molding). | Very low; long heating and cooling cycles — typical batch production. |
| Unit Cost Structure | High mold cost, low per-unit cost. Suitable for mass production to amortize tooling. | Low mold cost, high per-unit cost (driven by time and energy). Ideal for low-volume/custom production. |
| Typical Products | Packaging: Beverage bottles, shampoo bottles, medicine vials, oil drums. Industrial: Automotive ducts, fuel tanks, toys. | Industrial/Consumer: Large water tanks, septic tanks, kayaks, buoys, traffic cones, large dolls, automotive air cleaner housings, medical device enclosures. |
What is Blow Molding?
Blow molding, like the art of "blowing up balloons" with plastic, is a core process for efficiently manufacturing hollow plastic products. Its principle is simple yet ingenious: first, heated and softened plastic is formed into a tubular preform, placed in a mold, and then high-pressure air is injected into it, causing the plastic to inflate like a balloon, cooling and solidifying against the inner wall of the mold, ultimately forming the various bottles, buckets, cans, and other containers we see every day.
The brilliance of this technology lies in its combination of efficiency and flexibility. From perfume bottles of a few milliliters to industrial storage tanks of hundreds of liters, from thin beverage packaging to complex automotive fuel tanks, blow molding can achieve mass production with extremely fast production speeds and relatively low unit costs. Modern processes have further developed into different branches such as extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding, respectively meeting diverse needs for cost, precision, and strength.
Blow Molding Principle
Present Forming: Thermoplastic plastic (such as PET, PE, PP) is heated and melted to form a tubular, soft plastic preform.
Closed Inflation: The preform is placed in a two-part closed mold, and high-pressure air is injected into it through an air blower, causing the preform to inflate like a balloon until it completely adheres to the cold inner wall of the mold.
Cooling and Demolding: The plastic rapidly cools and solidifies within the mold. Once the mold is opened, the molded product can be removed, and excess material is trimmed.
Three Categories of Blow Molding
Based on the preform fabrication method, blow molding is mainly divided into three categories:

Advantages and Disadvantages of Blow Molding
Advantages:
Can produce hollow, complex shapes: Can mold hollow, three-dimensional products that are difficult to achieve with other processes in a single operation.
Seamless or fewer seams: Strong product integrity.
High production efficiency: Especially suitable for large-scale continuous production.
Good cost-effectiveness: Very low unit cost at high volumes.
Disadvantages:
High initial investment: Molds (especially injection blow molding) are expensive.
Challenges in wall thickness control: In extrusion blow molding, the preform sags due to its own weight, which may lead to uneven wall thickness at the top and bottom of the product.Design limitations: Usually cannot mold completely closed hollow bodies (air inlets must be provided).
What is Rotational Molding?
Rotational molding is a plastic molding art that uses rotation as a pen and heat as ink. It abandons the extrusion and stamping methods of traditional processes. Plastic powder is placed into a hollow mold, which is then heated evenly in a biaxial rotational dance, causing the material to adhere layer by layer to the inner wall like a mural, ultimately cooling into a seamless, uniformly thick hollow product.
The essence of this process lies in its ultimate freedom and inclusiveness. It does not rely on high pressure, so the mold can be welded from thin steel plates, freeing the development of large yacht hulls or irregularly shaped medical devices from heavy cost constraints; it is not bound by parting lines, achieving the natural airtightness of chemical storage tanks; it accommodates complex designs, allowing double-walled insulated boxes and children's slides with built-in structures to move from drawings to reality.
Core Principles of Rotational Molding
Its process can be compared to "making hollow chocolate balls":
Feeding: Precisely measured plastic powder (usually polyethylene PE) is placed into a thin-walled metal mold.
Heating and Rotation: The mold is closed and placed in a heating chamber. The mold rotates slowly around two mutually perpendicular axes simultaneously.
Clad forming: During rotation, the powder gradually melts upon heating and, under centrifugal force, is evenly coated and adheres to the entire inner wall of the mold.
Cooling and setting: The mold then enters a cooling chamber, where it solidifies and sets while continuing to rotate.
Mold opening and part removal: The mold stops rotating and opens, allowing the removal of the fully formed, seamless, one-piece product.
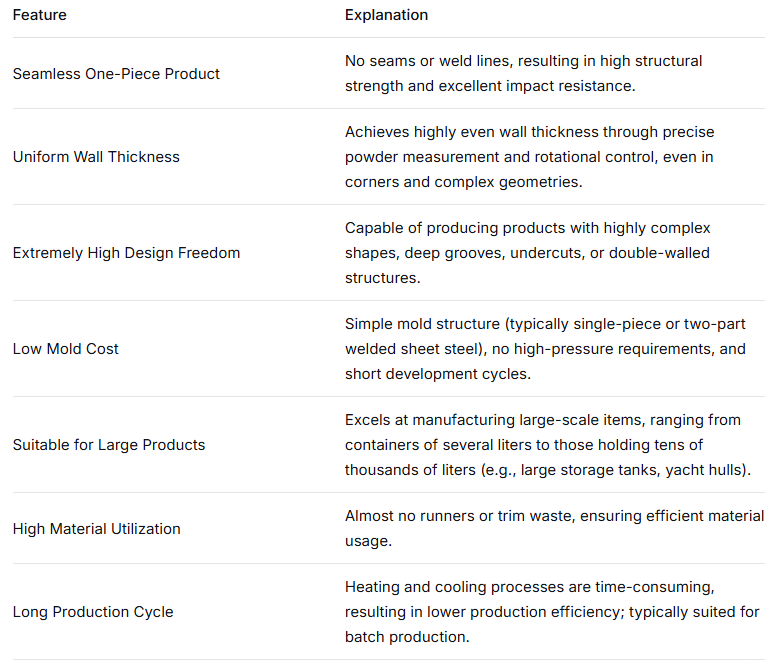
Rotational Molding Applications
Due to its unique advantages, rotational molding is mainly used in the following fields:
Large Containers: Water tanks, septic tanks, agricultural liquid storage tanks, chemical containers.
Transportation Components: Kayaks, small boat hulls, floating platforms, automotive ventilation ducts, fuel tanks.
Outdoor and Amusement Equipment: Large toys, slides, traffic cones, lampshades, seats.
Industrial Housing: Equipment enclosures, medical equipment housings, cleaning boxes.
How to Choose Between Blow Molding and Rotational Molding for My Project
Choosing between blow molding and rotational molding for your project is a critical decision that directly affects product performance, cost, development cycle, and market success. Below is a set of comparative tables:
| Evaluation Dimension | Your Project Requirements | Process Indication |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Annual Volume / Scale | □ Very large (>100k units) □ Medium □ Small batch / Custom (<5k units) | Large → Blow Molding Small → Rotational Molding |
| 2. Product Size | □ Small/medium (typically <200L) □ Large/oversized (>500L) | Small → Blow Molding Large → Rotational Molding |
| 3. Design Complexity | □ Standard shape, parting lines acceptable □ Complex geometry, deep grooves, double walls, seamless | Simple → Blow Molding Complex → Rotational Molding |
| 4. Performance Requirements | □ Lightweight, transparent, high gloss □ Heavy-duty, impact-resistant, weatherproof, seamless | Former → Blow Molding Latter → Rotational Molding |
| 5. Budget & Timeline | □ High mold investment budget, pursuing lowest unit cost □ Limited upfront investment, acceptable higher unit cost | Former → Blow Molding Latter → Rotational Molding |
Why Choose WSRCNC as Your Partner
Choosing WSRCNC as a partner is based on its demonstrated professional synergy in the fields of blow molding and rotational molding. In project evaluation, we face multi-dimensional decisions regarding output, size, cost, and design complexity—whether it's large-scale standardized production requiring blow molding or customized large-scale products requiring rotational molding, WSRCNC can provide integrated solutions that combine process understanding and cost optimization. Its value lies not only in technical execution but also in guiding clients through the fog of process selection via prototype verification, accurate pricing, and full-cycle cost analysis, enabling data-driven decision-making. It is this ability to balance efficiency and flexibility, focusing on solving the fundamental problems of manufacturing, that makes it a trustworthy partner from concept to mass production.









